This section is for those who want to do something with the library itself.
- Library's architecture
- How to: Adding new embedded platform
- How to: Adding new cryptographic backend
- How to: Compile as static archive
- How to: Run unit tests
- How to: Run static analysis
- How to build documentation
- How to run code formatter
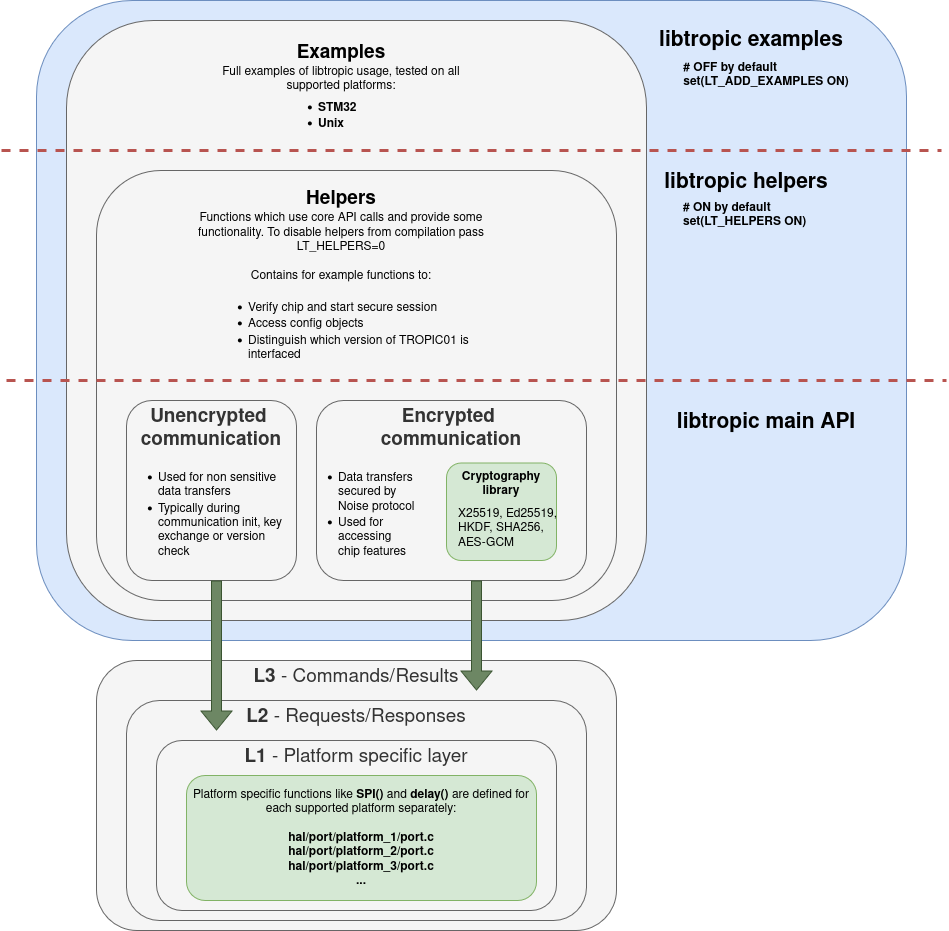
Library's architecture
Library architecture explained: core, examples, helpers, layers, hal, …
“Libtropic is standalone library expected to be used within a parent project”
How to: Adding new embedded platform
To add a new embedded platform, follow these steps:
- Implement the necessary HAL (Hardware Abstraction Layer) functions, according to
include/libtropic_port.h - Test the integration by compiling hello world example within your project
For more inspiration check out our Integration examples.
How to: Adding new cryptographic backend
As the libtropic was designed with extensibility in mind, it is possible to add a new backend for cryptographic operations.
The new backend has to support operations with:
- AES (GCM)
- encryption
- decryption
- ED25519
- signing
- SHA256
- hashing
- Curve25519
- multiplication on both arbitrary and base point
Guide
To add a new backend (let's say mycrypto), you need to:
- Create a new directory in
hal/cryptocalledmycrypto. - Create 4 source files in this directory:
lt_crypto_mycrypto_aesgcm.clt_crypto_mycrypto_ed25519.clt_crypto_mycrypto_sha256.clt_crypto_mycrypto_x25519.c
- In each of the source files, implement all required functions. The functions are declared in respective headers in
src/:lt_aesgcm.h: AES-GCM functions,lt_ed25519.h: ED25519 functions,lt_sha256.h: SHA256 functions,lt_x25519.h: Curve25519 functions.- Look into each of the headers. Purpose of every function is described in its comment. Copy function declarations from the headers to the sources and implement the functions. For exmple, to implement Curve25519 functions, I will copy declarations from the
lt_x25519.htolt_crypto_mycrypto_x25519.cand provide implementations. You can use existing ports for inspiration.
- Edit main CMakeLists --> see following section.
- Done. The new crypto backend can be enabled by passing
-DLT_CRYPTO_MYCRYPTOto the CMake.
Editing CMakeLists
In the Setup section, add new option:
At the bottom of the Setup section, there are checks for definition of cryptographic backend. Add your new backend to the checks:
In the Collect files section, add the new implementation files to compilation. Use this template, modify it accordingly, and paste it above the add new crypto sources above this line comment:
At last, in the Compile and link section, compile and link dependencies to your new crypto backend:
How to: Debug
For compiling in debug mode replace cmake .. with cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug .. (this will allow to step through with a debugger).
How to: Compile as static archive
Note: When compiling the library standalone as a static archive, a cryptography provider must be defined through cmake -D arguments
Compile libtropic as a static archive under Unix:
Cross-compile libtropic as a static archive:
How to: Run unit tests
Unit tests files are in tests/unit/ folder. They are written in Ceedling framework, install it like this:
Then make sure that you have correct version:
For now we support Ceedling version 0.31.1 only.
Once ceedling is installed, run tests and create code coverage report:
Randomization
Some tests use a rudimentary randomization mechanism using standard C functions. The PRNG is normally seeded with current time. Used seed is always printed to stdout. You can find the seed in logs (build/gcov/results/...).
To run tests with fixed seed, set RNG_SEED parameter to your desired seed (either directly in the file, or in the project.yml section :defines:). This is useful mainly to replicate a failed test run – just find out what seed was used and then set RNG_SEED to this.
How to: Run static analysis
To run static analysis, follow these steps:
- Choose a static analysis tool (e.g., cppcheck, clang-tidy).
- Configure the tool to analyze the library code.
- Run the analysis and review the reported issues.
How to build documentation
To build html documentation, you need Doxygen. The documentation is built using these commands:
The documentation will be built to: build/docs/doxygen/html. Open index.html in any recent web browser.
Notes:
- We tested Doxygen 1.9.1 and 1.9.8.
- PDF (LaTeX) output is not supported.
How to run code formatter
Following instructions are applicable on linux based machines:
Download <tt>clang-format-17.0.6</tt>
Choose version for your OS here, download it and extract it. Then add its path into your .bashrc file:
Reload .bashrc file:
Installed version might be checked like this:
For usage within VSCode, install clang-format extension for VSCode and restart IDE. You can then run formatter by right clicking on the code and choosing Format document->Clang Format.
To format particular folder use following prompt: